— SERVICES —
Adult Hearing Assessment
Comprehensive Hearing Assessment for adults
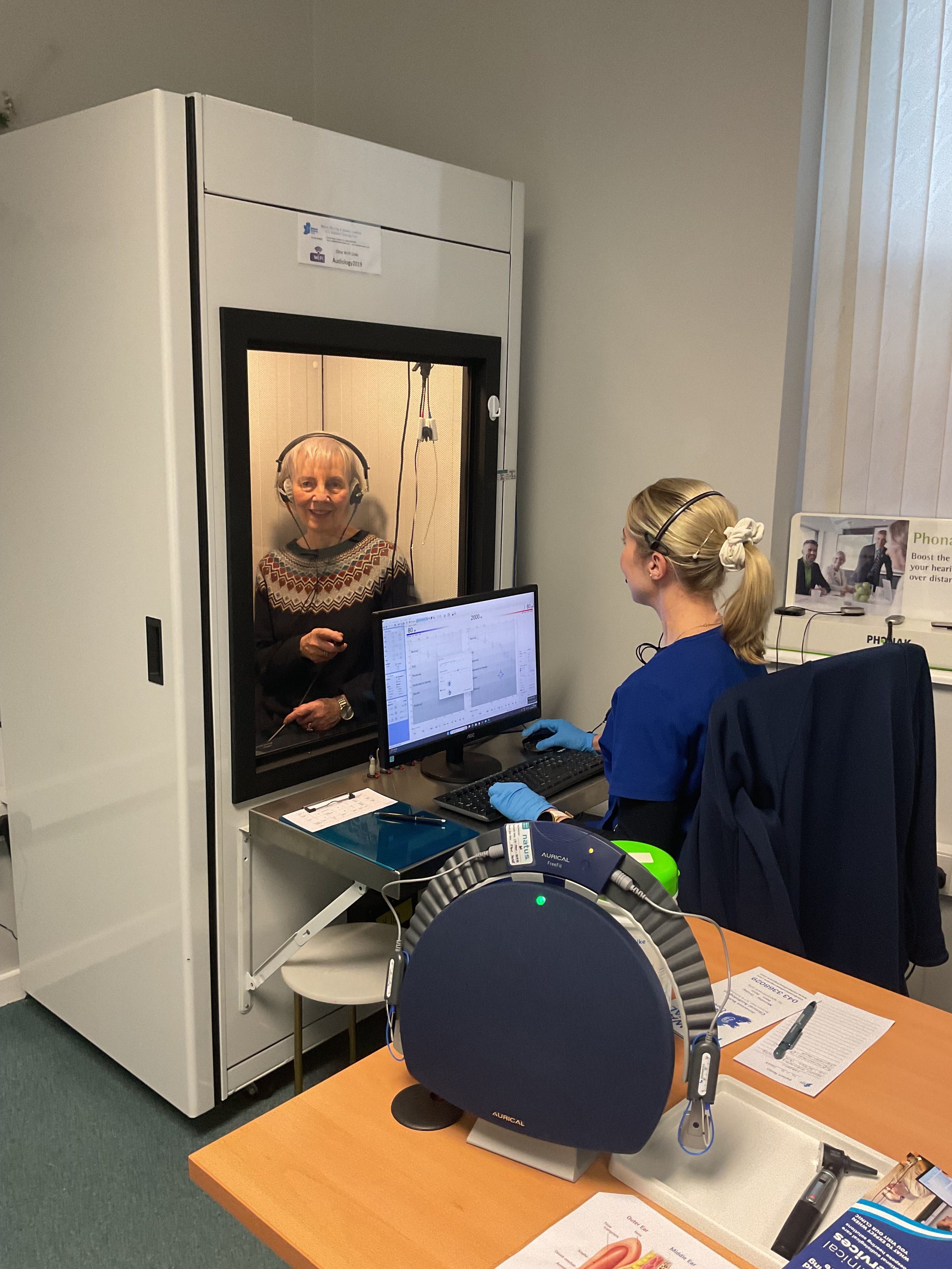
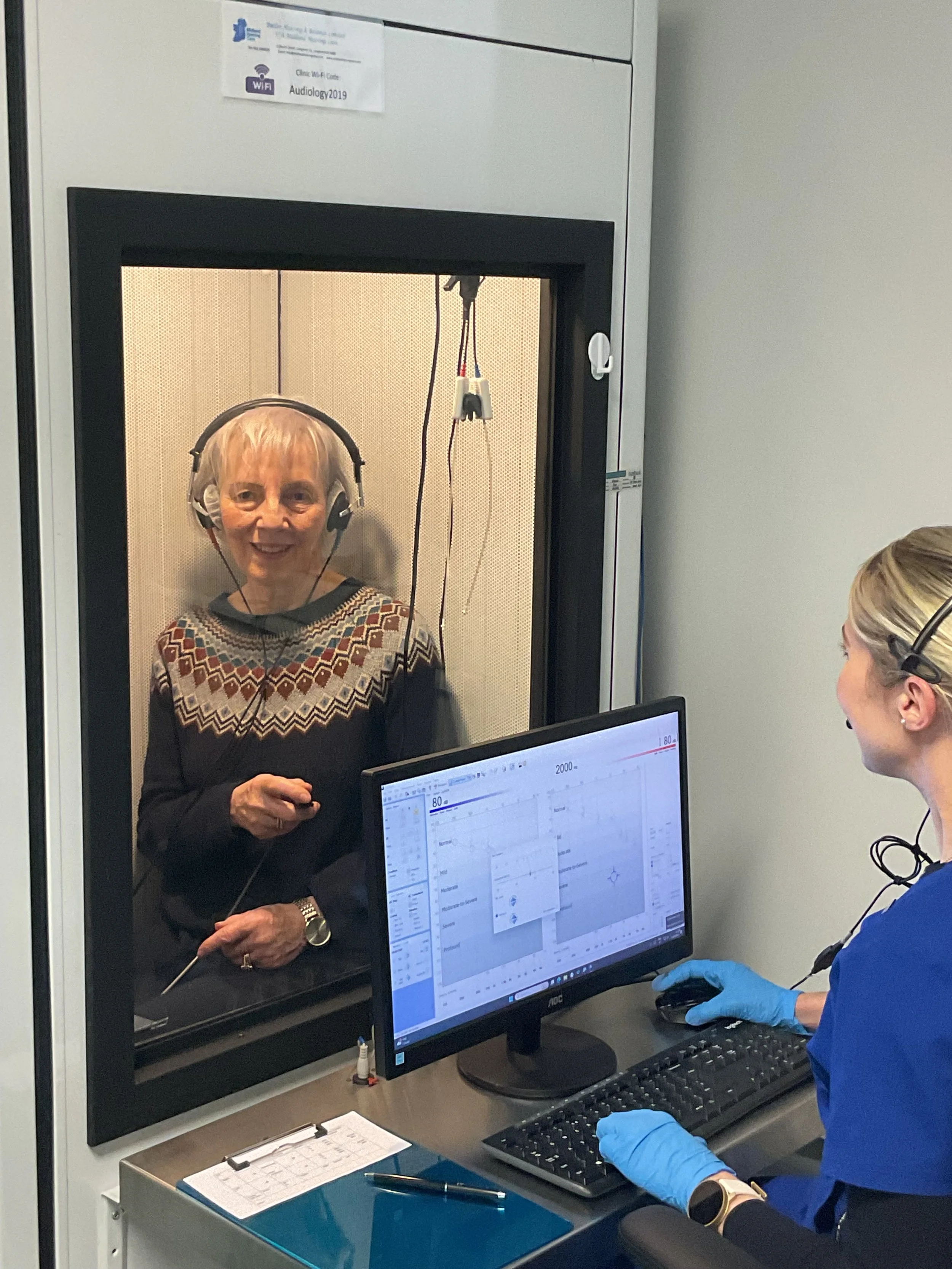
Pure-Tone Audiometry: is the most common audiology hearing test used in diagnostic audiology and is considered the gold standard of the audiology test battery. This hearing test is conducted in a sound-proof booth. During the test, a series of tones with varying pitches are presented through calibrated headsets or insert earphones. The tones start at a comfortable listening level and gradually decrease until they are no longer audible. The level where the tone is perceived 50% of the time is identified as the 'minimum hearing threshold' or the quietest level of hearing. Patients indicate when they hear a tone by pressing a button or raising their hand. The results are plotted on a hearing test chart or audiogram, providing essential data for a comprehensive hearing test.
Uncomfortable Loudness Level (LDL): also known as loudness discomfort level (LDL), is a crucial measurement in many audiology hearing tests, especially during hearing assessments for adults and seniors. This test helps audiologists counsel patients who may be suitable for hearing aids or those dealing with tinnitus or hyperacusis (sensitivity to loud sounds). The LDL is measured to determine the patient’s dynamic range of hearing, which spans from the softest sound they can hear to the loudest they can tolerate, typically over 85dB+. A tone is presented at a comfortable level around 70dBHL (decibel hearing level) and increased in 10dB steps until the patient signals when the sound becomes too loud or uncomfortable.
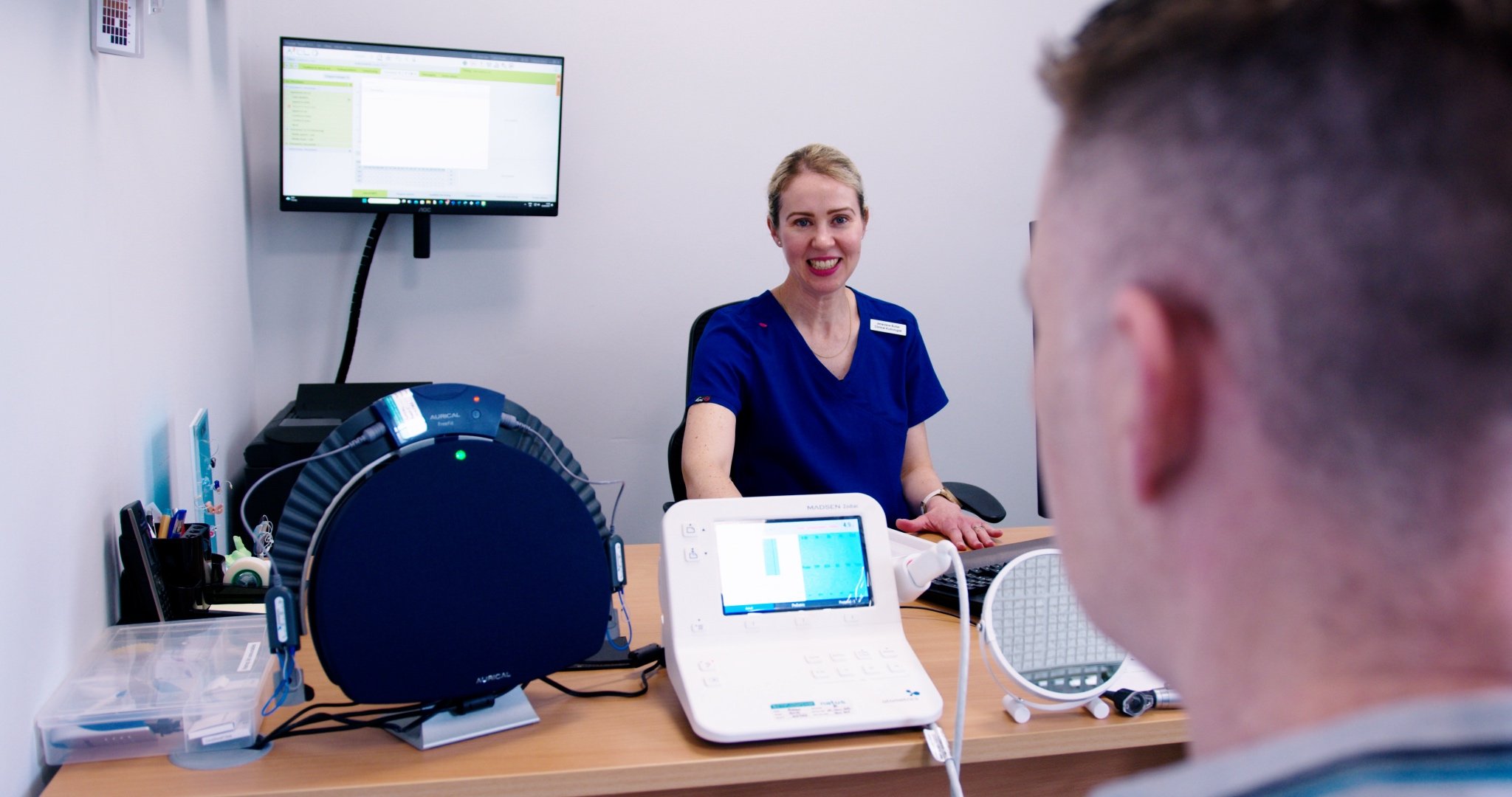
Adult hearing assessment in a sound-proof booth
Speech Audiometry: also known as a Speech Discrimination (SD) test or Word Recognition Score (WRS), is another key component of a comprehensive hearing assessment test. Speech audiometry tests measures how well a patient understands speech when it's loud enough to be heard comfortably through headsets or insert earphones. The audiologist instructs the patient to repeat words heard from a pre-recorded speech sample of phonetically-balanced words or words presented by the audiologist’s live voice. Speech audiometry tests provides vital information for understanding and processing speech as part of a comprehensive hearing test for adults and the elderly.
Speech in Noise (QuickSIN): is a specialized speech in noise test that evaluates how well a patient can understand speech in the presence of background noise. During the speech in noise test, the audiologist presents a short sentence through the headset or insert earphones with simulated background noise (like a busy café). This speech in noise test comprises six sentences and measures the patient’s ability to 'fill in the gaps' when hearing in noise. It provides a quick, yet accurate measurement of a patient’s hearing ability in noisy environments, essential for a comprehensive hearing test.
Bone Conduction Audiometry: is a specialized audiology test used to assess the type and level of hearing loss. In this test, tones are presented through a bone conductor headband placed behind the test ear, and the patient responds by pressing a button when they hear the tone. This method bypasses the middle ear, allowing sound to move directly from the outer ear to the inner ear and hearing nerve. Depending on the results, tones may need to be 'masked' with white noise presented to the non-test ear through a headphone, to ensure that the true thresholds of the test ear are measured.
The results, plotted on an audiogram, can confirm whether the patient has normal hearing or an underlying hearing loss. Bone conduction audiometry helps to classify hearing loss into one of three categories: such as conductive hearing loss (temporary), sensorineural hearing loss (permanent inner ear or neural loss), or mixed hearing loss (a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss). This is an essential part of any hearing test for adults and elderly patients experiencing hearing difficulties.